Click to view interactive map
![]()
Adequate antifungal therapy is a critical determinant of survival in patients admitted to an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) with suspected or proven fungal infections. Critical illness can alter the way human body handles antifungal agents, i.e. how the drugs are distributed in the body and removed from the body. Consequently, these changes can increase the risk of inappropriate antifungal exposure that may lead to
adverse consequence on patients' outcome. Developing an evidence-based antifungal dosing guideline is of global significance and should be considered a priority to improving clinical outcomes for patients receiving antifungal agents.
The aim of the SAFE-ICU Study is to develop optimised antifungal dosing guidelines for ICU patients with life-threatening infections that account for patient characteristics.
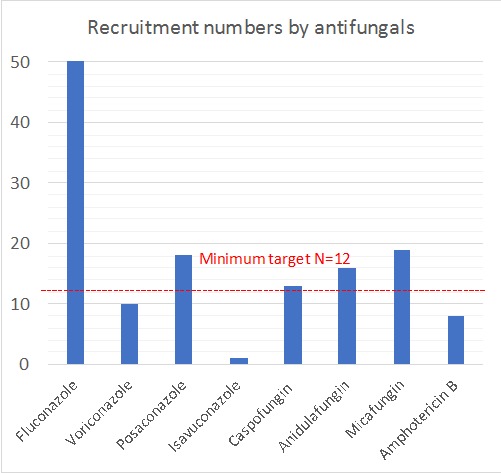
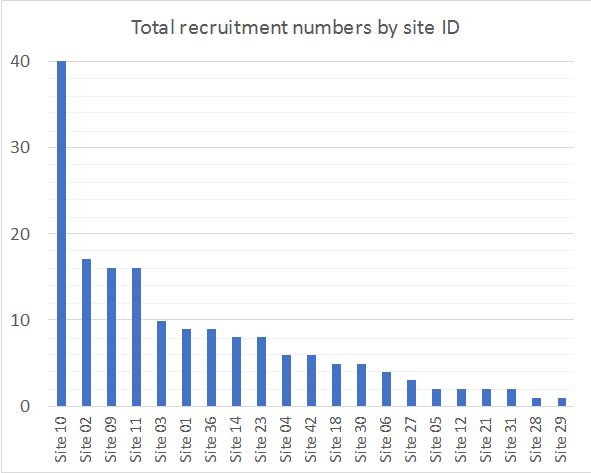
This is a multi-national study and will enrol ICU patients who are prescribed an antifungal agent (fluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, isavuconazole, caspofungin, anidulafungin, micafungin or amphotericin B). A minimum of 12 patients per drug will be enrolled across at least 15 countries and up to 80 ICUs.
3. Study contacts
Dr David Liu davel@itee.uq.edu.au